1 背景
已经学习这么长时间了,所以开始实战分析一个经典APP人人9.3.8版本,虽然该软件因缺乏维护已经无法很难进行修改密码等操作,但是其中登录协议的设计还是耐人寻味的,有一定的借鉴意义。
2 使用Fiddler抓取登录的数据包
首先,进入登录界面输入用户名和密码,如图1所示。
点击登录按钮后即可使用Fiddler抓取到具体的数据包,如图2所示。
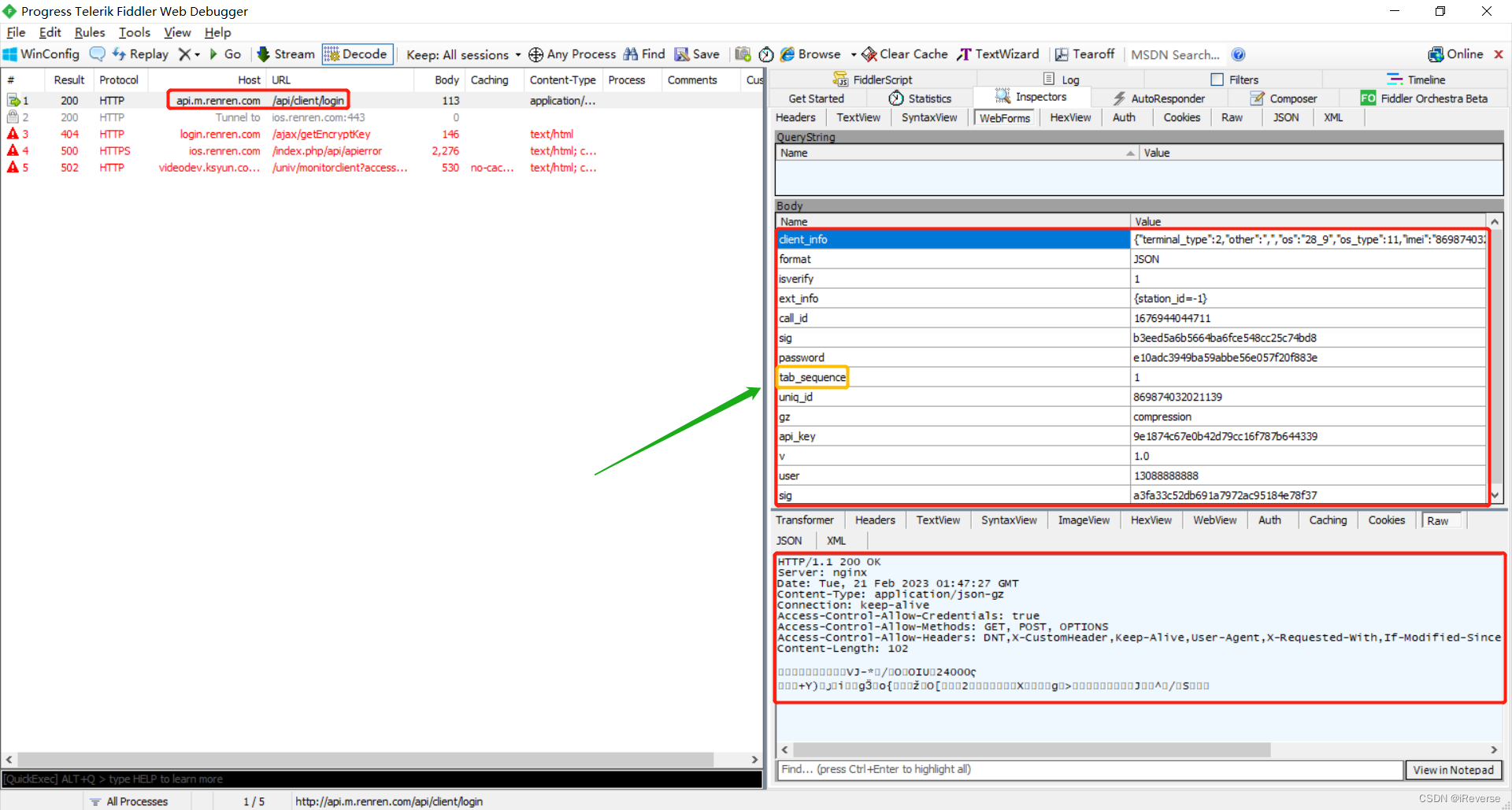
通过分析图2中的web表单,我们可以查看到一些字段信息,可以看见提交的字段和服务器返回的字段,我们一般搜索长字段,这样更好定位。Body中的值会发送到服务器,此处发现字段tab_sequence比较少见,我们下一阶段可以在Jadx中分析哪里调用了这个字段。
3 静态分析程序运行流程
3.1 Jdax反编译APK文件
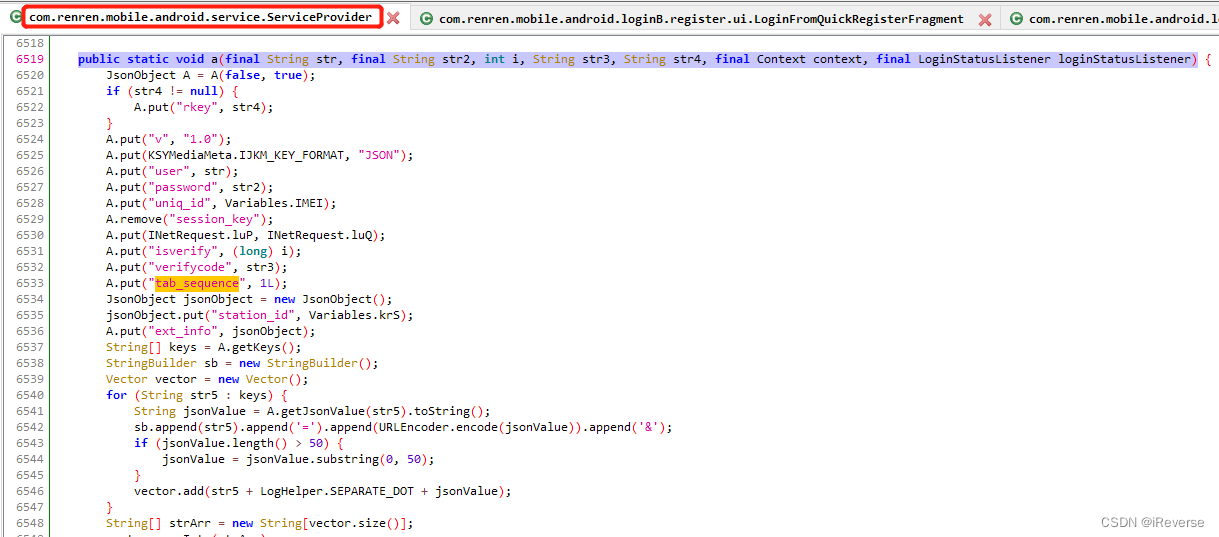
接着,使用Jadx打开人人.apk文件,并全局搜索tab_sequence的调用,最终只是在com.renren.mobile.android.service.ServiceProvider的方法a()中找到了对tab_sequence的调用,如图3所示。
然后,我们通过溯源分析,查看方法a()的调用处,如图4所示,这里有20处调用。
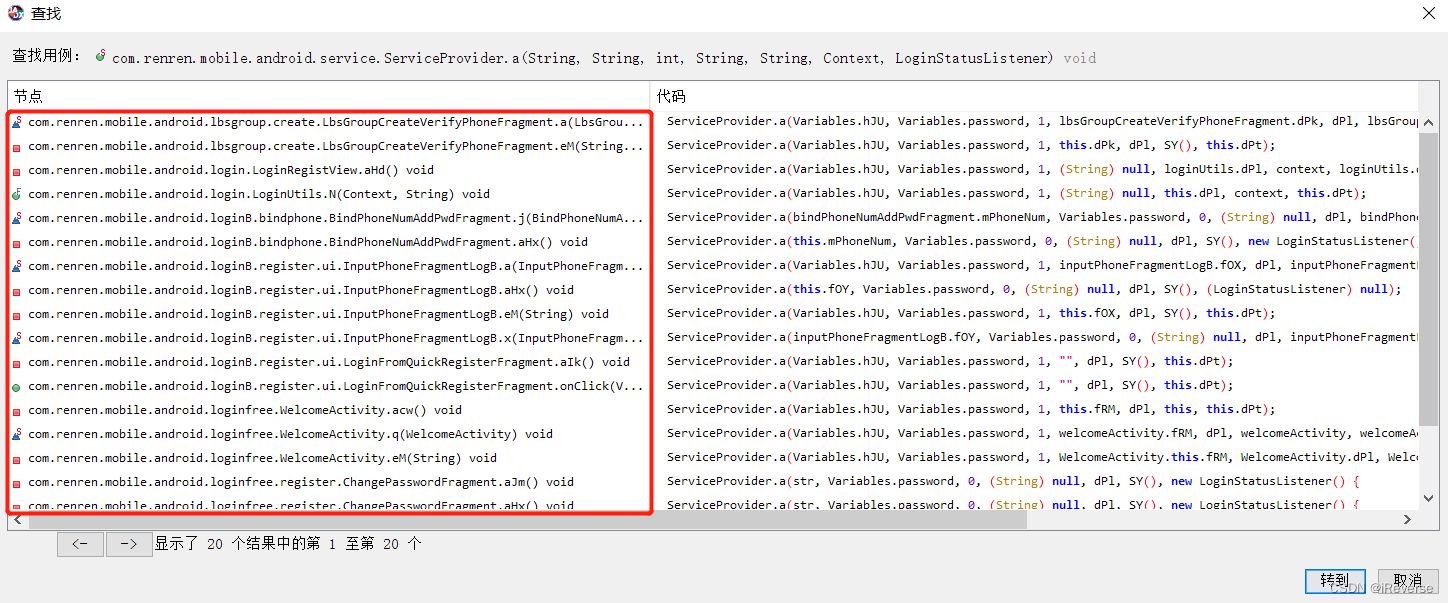
到了这里我们就有两种继续分析的思路,其一是一个个的去查看调用的情况,这样或许可以找到思路;另外也可以使用Android Device Monitor来分析点击登录按钮后调用的方法即方法剖析。
3.2 使用DDMS进行方法剖析
首先,我们使用AndroidKiller通过搜索tab_sequence找到方法a()的定义处,然后在开头插入方法剖析的smali代码,如图5所示。
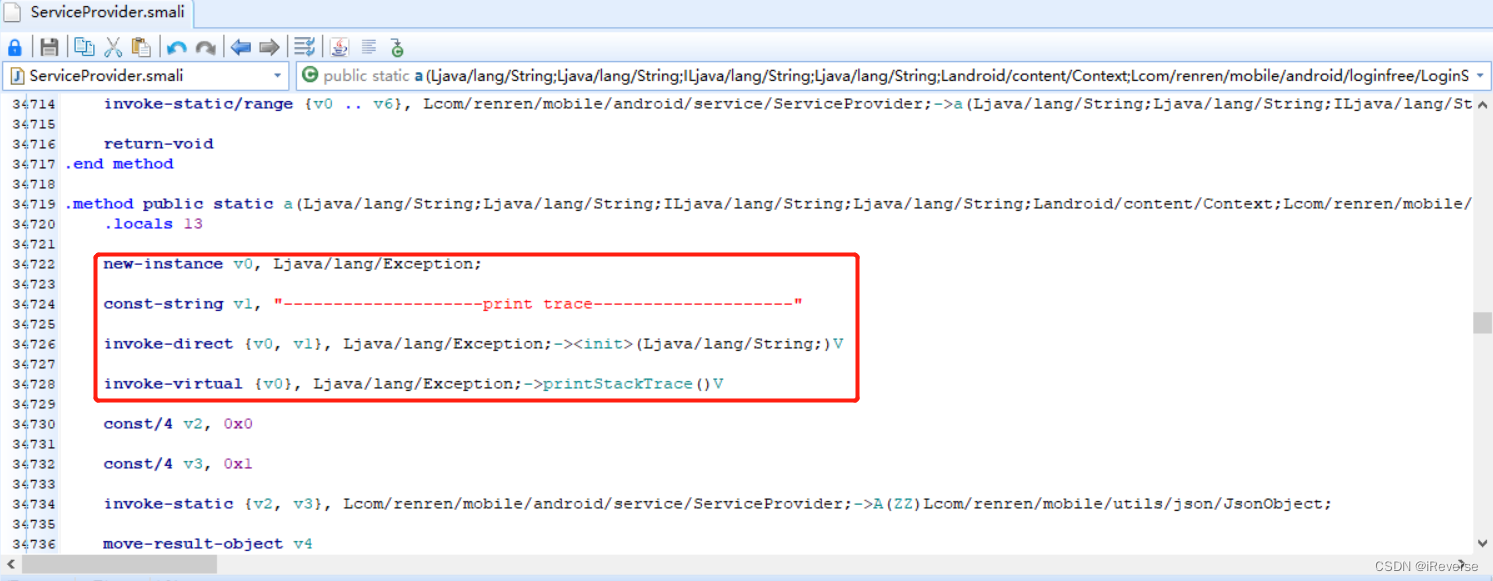
接着,将编译好的APK文件重新安装到真机中,在图1中的界面中重新输入用户名和密码并点击登录按钮。
另外,在DDMS过滤出只有人人的栏目,最终就能查看到图6中的方法剖析结果。
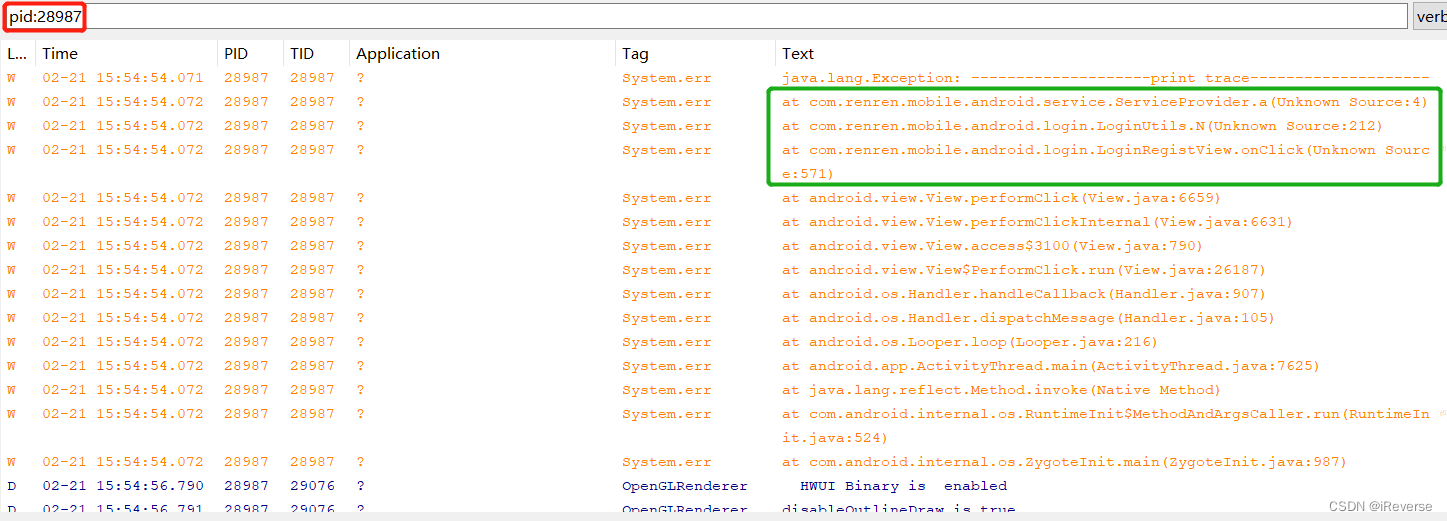
通过图6的结果可知,在点击登录按钮之后,方法com.renren.mobile.android.login.LoginRegistView.onClick()调用了方法com.renren.mobile.android.login.LoginUtils.N(),方法com.renren.mobile.android.login.LoginUtils.N()调用了方法com.renren.mobile.android.service.ServiceProvider.a()。
3.2 Jadx分析登录协议的具体实现
回到OnClick函数(com.renren.mobile.android.login.LoginRegistView.onClick()),通过分析可知图7中的代码就是点击登录按钮执行的代码。
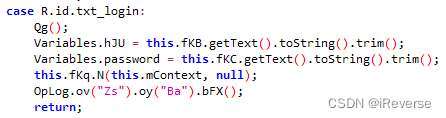
这里从用户名和密码框取出字符保存在类Variables的属性hJU和password中,然后调用了N函数(com.renren.mobile.android.login.LoginUtils.N()),进入N函数,如图8所示。
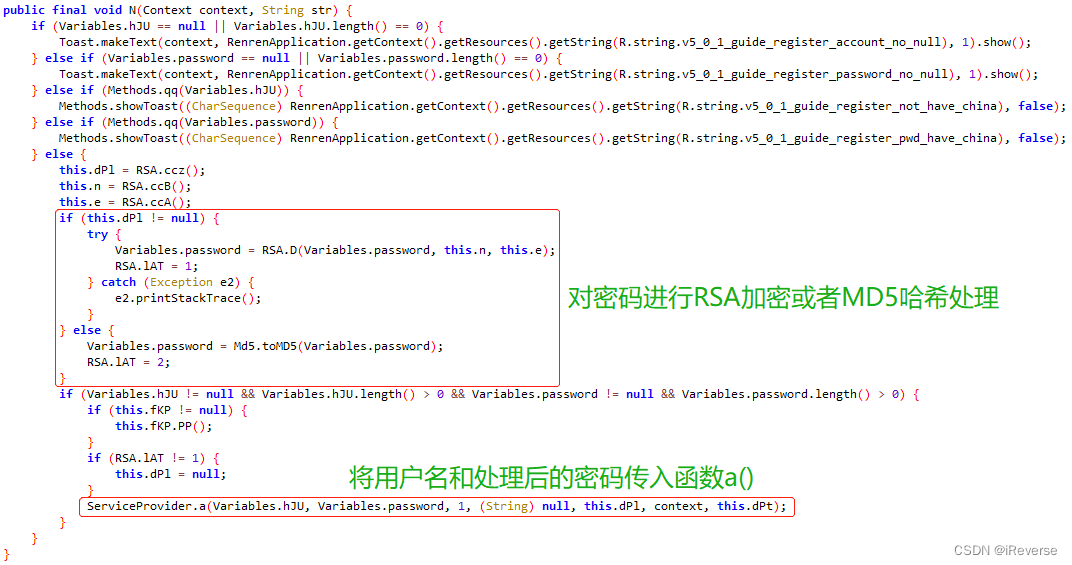
函数N()主要是对用户输入的用户名和密码进行处理,然后将处理后的值作为函数a()的参数进行调用,接下来跟进函数a(),如下面代码所示。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| public static void a(final String str, final String str2, int i, String str3, String str4, final Context context, final LoginStatusListener loginStatusListener) {
JsonObject A = A(false, true);
if (str4 != null) {
A.put("rkey", str4);
}
A.put("v", "1.0");
A.put(KSYMediaMeta.IJKM_KEY_FORMAT, "JSON");
A.put("user", str);
A.put("password", str2);
A.put("uniq_id", Variables.IMEI);
A.remove("session_key");
A.put(INetRequest.luP, INetRequest.luQ);
A.put("isverify", (long) i);
A.put("verifycode", str3);
A.put("tab_sequence", 1L);
JsonObject jsonObject = new JsonObject();
jsonObject.put("station_id", Variables.krS);
A.put("ext_info", jsonObject);
String[] keys = A.getKeys();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Vector vector = new Vector();
for (String str5 : keys) {
String jsonValue = A.getJsonValue(str5).toString();
sb.append(str5).append('=').append(URLEncoder.encode(jsonValue)).append('&');
if (jsonValue.length() > 50) {
jsonValue = jsonValue.substring(0, 50);
}
vector.add(str5 + LogHelper.SEPARATE_DOT + jsonValue);
}
String[] strArr = new String[vector.size()];
vector.copyInto(strArr);
A.put("sig", a(strArr, jhS));
AnonymousClass2 r2 = new INetResponse() {
/* class com.renren.mobile.android.service.ServiceProvider.AnonymousClass2 */
private static /* synthetic */ boolean $assertionsDisabled = (!ServiceProvider.class.desiredAssertionStatus());
@Override // com.renren.mobile.net.INetResponse
public final void response(INetRequest iNetRequest, JsonValue jsonValue) {
if (LoginStatusListener.this != null) {
LoginStatusListener.this.b(iNetRequest, jsonValue);
}
if (!$assertionsDisabled && jsonValue == null) {
throw new AssertionError();
} else if (jsonValue instanceof JsonObject) {
JsonObject jsonObject = (JsonObject) jsonValue;
if (!Methods.noError(iNetRequest, jsonObject)) {
long num = jsonObject.getNum("error_code");
String string = jsonObject.getString(BaseObject.ERROR_DESP);
String string2 = jsonObject.getString("click_url");
if (LoginStatusListener.this != null) {
LoginStatusListener.this.b(num, string, string2);
}
if (num == -99 || num == -97) {
Methods.showToast((CharSequence) "无法连接网络,请检查您的手机网络设置...", false);
return;
}
return;
}
Variables.hJU = str;
Variables.password = str2;
Variables.loginType = 0;
try {
((AccountDAO) DAOFactory.getInstance().getDAO(DAOFactory.DAOTYPE.ACCOUNT)).deleteAccount(context, jsonObject.getNum("uid"));
} catch (NotFoundDAOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ServiceProvider.b(jsonObject, context);
TalkManager.INSTANCE.initUserInfo(RenrenApplication.getContext(), Variables.user_name, Variables.user_id, ServiceProvider.jhT, true);
new StringBuilder("isGuideUser = ").append((int) jsonObject.getNum("is_guide"));
SharedPreferences.Editor edit = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(context).edit();
edit.putBoolean("is_new_account_login", true);
edit.commit();
ServiceProvider.a(new INetRequest[]{ServiceProvider.iU(true), ServiceProvider.iT(true)}, true);
LoginStatusListener.this.onLoginSuccess();
ServiceProvider.buf();
}
}
};
HttpRequestWrapper httpRequestWrapper = new HttpRequestWrapper();
httpRequestWrapper.setUrl(jgH + "/client/login");
httpRequestWrapper.setData(A);
httpRequestWrapper.setResponse(r2);
httpRequestWrapper.setSecretKey(jhS);
HttpProviderWrapper.getInstance().addRequest(httpRequestWrapper);
}
|
通过分析上面代码可知,方法a()首先将POST表单提交的所有数据都存储在JsonObject类A中,sig是用前面所有字段和secreKey的值进行排序组合后计算MD5值,然后通过HttpRequestWrapper将数据发送到服务器。
4 Android Studio动态调试
首先使用AndroidKiller反编译APK文件,然后使用Android Studio导入反编译出来的工程文件,接着依次设置Sources Root、Project SDK、Remote JVM Debug,下一步在cmd中输入下列命令
adb shell am start -D -n com.renren.mobile.android/com.renren.mobile.android.ui.WelcomeScreen
adb shell ps | findstr “com.renren.mobile.android”
adb forward tcp:8700 jdwp:上一步的PID值
其次,我们就可以在com.renren.mobile.android.service.ServiceProvide.a()函数的httpRequestWrapper.setData(A);处下断点,然后就能看到JsonObject类A的对象的具体值,如图9所示。
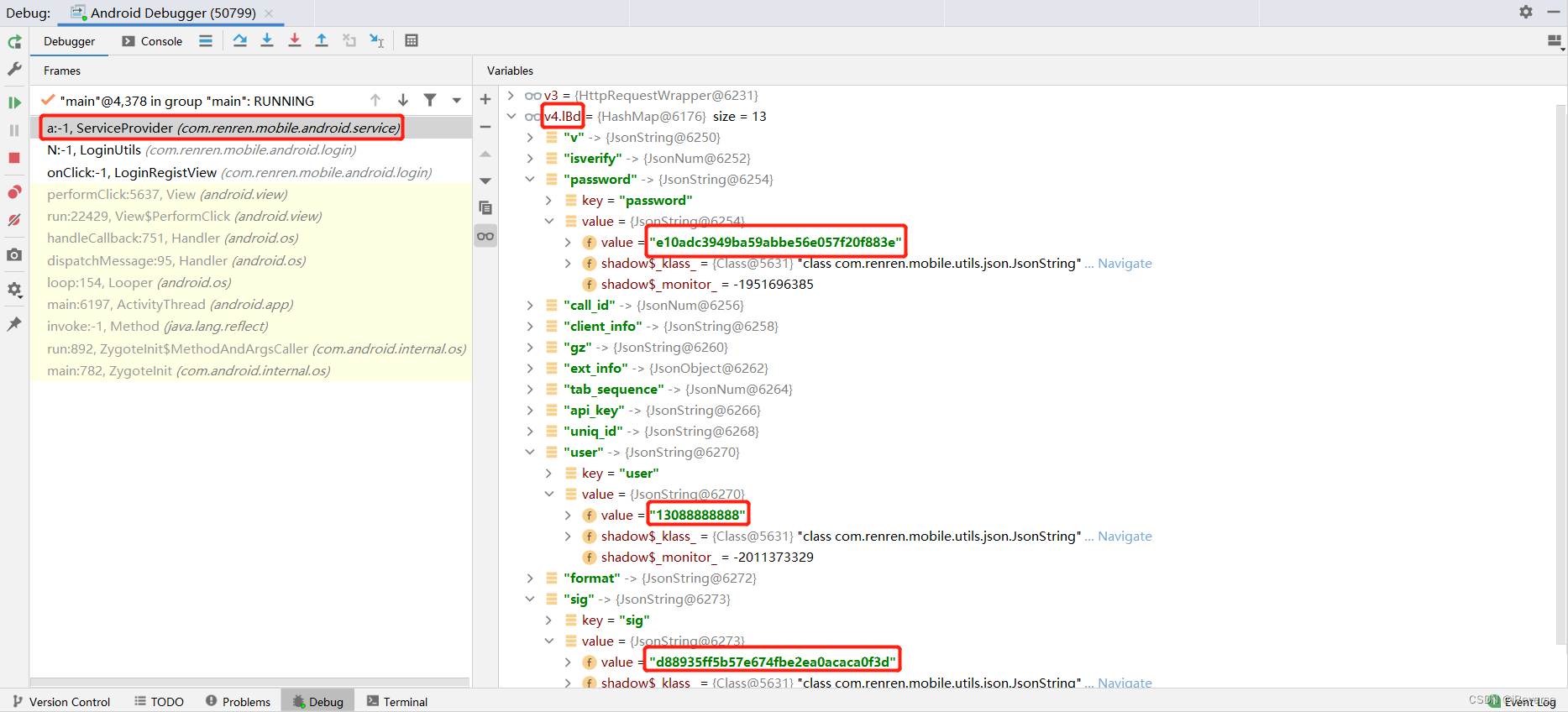
我们还可以通过下断点分析出点击登录按钮后具体的程序运行流程,此处略过。
5 总结
这里基本上分析出人人视频的登录协议,首先使用Fiddler分析点击登录按钮后提交的字段,然后使用AndroidKiller和Jadx查看某些特殊的字段,同时使用DDMS进行方法剖析,有时还可能需要使用IDA分析so层的代码,从而找到关键逻辑,最终Hook或者动态调试出Java层或so层的某些字段的值,这也是分析APK文件的常用思路。
6 参考文献
[1]https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-268451.htm
[2]https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33364733/article/details/100046422
[3]https://blog.csdn.net/YJJYXM/article/details/101678443
[4]https://blog.csdn.net/Yijin_/article/details/102474851
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达,可以邮件至 xingshuaikun@163.com。










