密码学课程设计-序列密码
发布时间 :
阅读 :
1 概述
序列密码(又称流密码)是一类重要的对称密码体制,它一次只对明文消息的单个字符(通常是二进制1位)进行加解密变换,具有算法实现简单、速度快、错误传播少等特点。
2 算法原理与设计思路

3 关键算法分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| # 字符串转二进制
def strtobin(str):
res = ""
for i in str:
tmp = bin(ord(i))[2:]
for i in range(0, 8 - len(tmp)):
tmp = '0' + tmp
res += tmp
return res
# 将字符串如ab转换成二进制0110000101100010,
# 线性反馈移位寄存器
def LFSR(ai, t):
t.append(t[1] ^ t[6])
t.pop(0)
return t
|
将t1和t6异或得到t0,然后再出栈。
4 运行结果
完整代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| # 线性反馈移位寄存器
def LFSR(ai, t):
t.append(t[1] ^ t[6])
t.pop(0)
return t
# 字符串转二进制
def strtobin(str):
res = ""
for i in str:
tmp = bin(ord(i))[2:]
for i in range(0, 8 - len(tmp)):
tmp = '0' + tmp
res += tmp
return res
def main():
print("请输入明文:")
plaintext = input()
plaintextLength = int(len(plaintext))
strlfsr = ""
# m序列 f(x) = x ** 8 + x ** 4 + x ** 3 + x **2 + 1
baseFunction = [1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1]
plaintextBin = strtobin(plaintext)
for a in range(plaintextLength):
# 移位寄存器中的初始值
posture = []
for j in range(8):
if plaintextBin[j] == '1':
posture.append(1)
elif plaintextBin[j] == '0':
posture.append(0)
t = list(posture)
# sum用来存储循环次数
sum = 1
for i in range(pow(2, len(baseFunction) - 1)):
strlfsr += str(posture[0])
print(LFSR(baseFunction, posture), '循环次数为', sum)
sum = sum + 1
if (t == posture):
if sum == pow(2, len(baseFunction)):
print("这是一个本原多项式,周期为:", sum - 1)
break
else:
print("这不是一个本原多项式,故周期不为:", 2 ** len(posture) - 1)
break
print('密文是:', strlfsr)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
|
运行效果如下图:
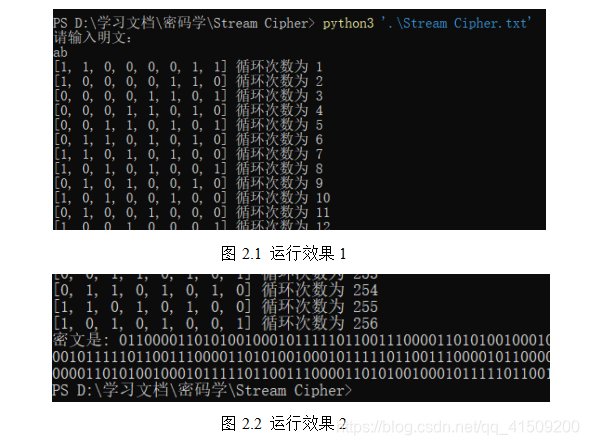
5 密码安全性分析
该加密算法对输入字符的ASCII码进行通过本源多项式进行处理,中间利用了一定的反馈函数,如果攻击者不知道反馈函数和本源多项式,那这种加密方法能够抵抗唯密文攻击,如果泄露了反馈函数和本源多项式,那这个加密系统很容易被破解。
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达,可以邮件至 xingshuaikun@163.com。



